In the world of mental health and well-being, there exists a diverse array of therapeutic approaches, each tailored to address specific challenges and conditions. One such approach, gaining significant recognition and popularity, is Behavioral Activation Therapy (BAT). This article will delve into the world of BAT, its principles, methodologies, and how it can be a transformative force in the lives of those struggling with depression and other mood disorders.
Contents
Introduction to Behavioral Activation Therapy
In the realm of mental health treatment, Behavioral Activation Therapy (BAT) has emerged as a beacon of hope for individuals grappling with depression and mood disorders. Unlike traditional therapies that delve into deep-rooted psychological issues, BAT focuses on the here and now, empowering individuals to regain control of their lives through specific behavioral changes.
Core Principles of Behavioral Activation Therapy

BAT aims to break this cycle and help individuals engage in more fulfilling and positive behaviors. Here are the core principles of Behavioral Activation Therapy:
- Activity Monitoring: In BAT, individuals are encouraged to monitor their daily activities and mood. They keep a record of what they do throughout the day and rate their mood before and after each activity. This helps them identify patterns and understand how their activities affect their mood.
- Activity Scheduling: The therapist and the individual work together to create a structured daily schedule that includes various activities, both routine tasks and enjoyable or meaningful ones. The goal is to increase the number of positive and rewarding activities in the person’s life.
- Graded Task Assignment: Behavioral Activation Therapy breaks down larger, daunting tasks into smaller, manageable steps. This makes it easier for individuals to engage in activities they may have been avoiding due to depression.
- Activity Hierarchies: Therapists and clients collaboratively create hierarchies of activities based on their level of difficulty and perceived pleasure. This helps individuals start with easier activities and gradually work their way up to more challenging ones.
- Identifying Avoidance Patterns: BAT helps individuals recognize and address avoidance behaviors. Depression often leads to avoidance of activities or situations that may trigger negative emotions. By identifying and confronting these avoidance patterns, BAT promotes increased engagement.
- Problem-Solving: BAT encourages problem-solving skills to overcome barriers to engaging in activities. This may involve addressing practical obstacles or working on cognitive and emotional barriers that prevent individuals from taking action.
The Therapeutic Process: How BAT Works?
Behavioral Activation Therapy (BAT) is a structured and evidence-based approach to treating depression. It works by helping individuals understand and change their behavior patterns to alleviate depressive symptoms. Here’s an overview of the therapeutic process and how BAT works:
Assessment and Goal Setting:
- The therapeutic process typically begins with an initial assessment by a trained therapist. This assessment helps identify the individual’s specific depressive symptoms, their severity, and the factors contributing to their depression.
- The therapist collaborates with the individual to set treatment goals. These goals may include reducing depressive symptoms, increasing daily functioning, and improving overall well-being.
Activity Monitoring:
- Individuals are asked to keep a daily record of their activities, including what they do throughout the day and how they feel before and after each activity. This activity monitoring helps identify patterns of behavior that contribute to or alleviate depressive symptoms.
Identifying Avoidance and Withdrawal:
- Through activity monitoring, individuals can recognize avoidance behaviors and withdraw from pleasurable or rewarding activities. These behaviors often play a significant role in maintaining depression.
- The therapist and individual work together to identify specific activities or situations that are being avoided due to depression.
Activity Scheduling:
- The therapist and client collaborate to create a structured daily schedule that incorporates a variety of activities, including routine tasks and activities that the individual finds enjoyable or meaningful.
- Activities are scheduled in a way that gradually increases the person’s level of engagement and includes activities from different life domains, such as work, social, and leisure.
Overcoming Barriers and Obstacles
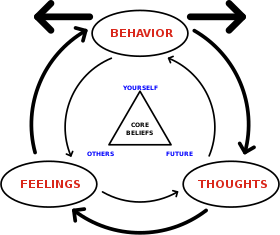
Overcoming barriers and obstacles is a crucial aspect of the therapeutic process, particularly in approaches like Behavioral Activation Therapy (BAT), which aims to help individuals with depression engage in more fulfilling and positive behaviors. Here are some common barriers and obstacles individuals may face during therapy and strategies to overcome them:
Lack of Motivation:
- Barrier: Depression often leads to a lack of motivation to engage in activities, making it difficult to initiate and sustain behavioral changes.
- Strategy: Start with small, manageable activities and gradually increase the level of engagement. Positive reinforcement and celebrating small successes can boost motivation.
Fear and Anxiety:
- Barrier: Anxiety and fear of failure or judgment can prevent individuals from attempting new activities or leaving their comfort zones.
- Strategy: Use graded task assignments to break down larger tasks into smaller, less intimidating steps. Practice relaxation techniques or mindfulness to manage anxiety.
Negative Self-Perception:
- Barrier: Low self-esteem and negative self-perception are common in depression, leading individuals to doubt their abilities.
- Strategy: Challenge and reframe negative self-talk with the help of cognitive-behavioral techniques. Focus on building self-compassion and self-acceptance.
Practical Obstacles:
- Barrier: Practical issues, such as lack of resources or time constraints, can hinder participation in desired activities.
- Strategy: Problem-solving skills can be used to address practical barriers. Identifying available resources, setting realistic goals, and making a plan can help overcome these obstacles.
Social Isolation:
- Barrier: Depression often leads to social withdrawal and isolation, making it challenging to engage in social activities.
- Strategy: Gradually reintroduce social activities, starting with low-pressure or one-on-one interactions. Seek support from a therapist or support group for social anxiety.
Cognitive Distortions:
- Barrier: Depressive thinking patterns, such as black-and-white thinking or overgeneralization, can hinder progress.
- Strategy: Cognitive-behavioral techniques can help individuals identify and challenge these distortions. Encourage a more balanced and realistic perspective.
The Future of Behavioral Activation Therapy
The future of Behavioral Activation Therapy (BAT) holds several promising developments and possibilities as it continues to evolve in the field of psychotherapy and mental health treatment:
- Integration with Technology: BAT may increasingly incorporate technology, such as mobile apps and wearable devices, to help individuals monitor their activities, set reminders for scheduled tasks, and receive feedback on their progress. These digital tools can enhance the self-monitoring and self-management aspects of BAT.
- Teletherapy and Remote Delivery: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of teletherapy and remote mental health services. BAT can be adapted for remote delivery, making it more accessible to individuals who have difficulty accessing in-person therapy.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Advances in data analytics and machine learning may enable therapists to create more personalized treatment plans based on an individual’s activity and mood patterns. This could lead to more tailored and effective interventions.
- Integration with Other Therapies: BAT can be integrated with other therapeutic approaches, such as mindfulness-based interventions, to create hybrid treatment protocols that address a broader range of mental health issues. Combining BAT with other evidence-based treatments may enhance its efficacy.
- Cultural Adaptations: Cultural adaptations of BAT may become more prevalent to ensure that the therapy is culturally sensitive and relevant to diverse populations. Therapists may customize the approach to better align with the values and beliefs of different communities.
Benefits of Behavioral Activation Therapy

Behavioral Activation Therapy (BAT) is an evidence-based approach primarily used in the treatment of depression, but it can also be applied to various other mental health conditions. BAT offers several benefits to individuals undergoing therapy:
- Effectiveness: BAT is supported by a substantial body of research demonstrating its effectiveness in reducing depressive symptoms. It is as effective as other established treatments for depression, such as Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and medication.
- Action-Oriented: BAT is an action-oriented therapy that focuses on behavior change. It helps individuals address the core issue of depression, which often involves a cycle of inactivity and withdrawal from pleasurable activities.
- Simple and Structured: BAT is relatively straightforward to understand. It involves monitoring daily activities, setting goals, and gradually increasing engagement in positive behaviors. This simplicity can make it accessible and practical for many individuals.
- Customization: BAT can be tailored to an individual’s unique needs and preferences. Therapists work collaboratively with clients to identify specific activities, values, and goals that are meaningful to the individual.
- Quick Onset of Improvement: BAT often leads to a relatively quick onset of symptom improvement. Clients typically begin to experience positive changes in mood and functioning within a few weeks of starting therapy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Behavioral Activation Therapy stands as a beacon of hope for individuals battling depression. Its structured approach, focus on behavior change, and emphasis on the present offer a path to a brighter, more fulfilling future.
Overall, Behavioral Activation Therapy is a highly regarded approach that offers numerous benefits for individuals struggling with depression or related mental health issues. Its focus on behavior change, simplicity, and customization make it a valuable tool in the field of psychotherapy.
If you are looking for an affordable Online Therapy TherapyMantra can help: Book a trial Online therapy session.


